


Next: Summary and conclusions
Up: Cherenkov angle reconstruction
Previous: Improved Cherenkov angle resolutions
Systematic cross-checks
Results from the two analyses indicate good agreement for both HPDs with and without filters. A summary of systematic
cross-checks and the methods used to ascribe systematic
uncertainties follows :
- HPD geometry and alignment - By studying the
dependence of the mean Cherenkov angle resolution in an event as a
function of the number of photons, an estimate of the residual
misalignment of the detector prototype is determined. This
corresponds to between 0.1 and
0.3 mrad for HPDs (2,3,5,6)
and (4,7) respectively.
- Radiator pressure variation - The resolutions given above are
determined from a subset of the data within which the pressure
variation of the mean Cherenkov angle is determined to be
0.02 mrad.
- Beam composition - The beam contamination cut on the
upstream Cherenkov counter is varied widely by changing the cut
applied on the output from the upstream Cherenkov counter.
The maximum effect observed on the mean Cherenkov angle resolution is
0.1 mrad.
- Noise contamination from the hit selection - The effect of
the default 4 sigma selection cut is studied by varying it from 3 to
5 sigma and determining the shift in the average Cherenkov
resolution. The shift is asymmetric due to the increasing noise
contamination when the cut is reduced to 3 sigma. As a conservative
value, the systematic error is estimated to be
0.1 mrad.
- Use of the geometrical fitting procedure - To check for a
systematic bias in the geometrical fitting method, a similar selection
of HPDs (4,7) is applied to that for (2,3,5,6) in order to
verify the stability of the measured resolutions. The procedure
followed is to use hits from HPDs 3 & 6 only. This is the
same but diametrically opposite configuration to HPDs 4
& 7. The hit multiplicities of (3,6) are then reduced to those of
(4,7) by randomly deleting hits, to emulate the effects of the mylar
coverings on HPDs (4,7). The results indicate that the effects
of the elliptical fitting method induce a maximum change in the
observed Cherenkov angle resolution of 0.08 mrad.
When combined with the total uncertainties, listed above, the
systematic error on the measured Cherenkov resolution is expected to
be of the order of between 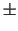 0.2 and
0.2 and
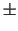 0.3 mrad for HPDs (2,3,5,6) and (4,7) respectively.
0.3 mrad for HPDs (2,3,5,6) and (4,7) respectively.



Next: Summary and conclusions
Up: Cherenkov angle reconstruction
Previous: Improved Cherenkov angle resolutions
latex2html conversion by www person on 2000-01-23