


Next: Simulation of the RICH-1
Up: Performance of a Prototype
Previous: Data selection criteria
Alignment of the silicon telescope
The beam telescope is used to provide an event-by-event track
direction for the Cherenkov angle reconstruction. To achieve this, the
alignment uncertainty of the telescope must be
significantly less than
0.4 mrad with respect to the RICH vessel.
Internal alignment of the telescope is achieved by selecting events with
precisely one hit in each plane and studying fit residuals with
respect to a straight line. External alignment is performed using
events with 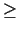 2 detected photons in the RICH. For measured
track slopes (mx, my) different from their true values :
2 detected photons in the RICH. For measured
track slopes (mx, my) different from their true values :
mxtrue = mx + 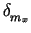 , and mytrue = my + , and mytrue = my + 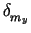 . .
|
|
then a shift of the measured Cherenkov angles is induced. By
minimising the spread in the measured Cherenkov angles, as a function
of
(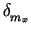 ,
, ), their optimum values are determined as shown in
Figure 7.
), their optimum values are determined as shown in
Figure 7.
Figure 7:
Variance of the measured Cherenkov angles as a function
of the constant offsets,
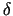 mx and
mx and
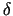 my, applied to
the gradient of the silicon telescope beam vector.
my, applied to
the gradient of the silicon telescope beam vector.
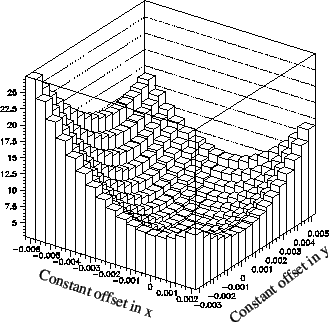 |
The values of
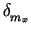 and
and
 which minimize the average variance
<
which minimize the average variance
< 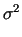 (
(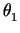 ,
,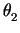 ,...,
,...,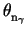 ) > are of the order of
) > are of the order of 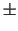 1 mrad,
and are used to correct the event-by-event beam direction
determined from telescope data.
1 mrad,
and are used to correct the event-by-event beam direction
determined from telescope data.



Next: Simulation of the RICH-1
Up: Performance of a Prototype
Previous: Data selection criteria
latex2html conversion by www person on 2000-01-23
![]() 2 detected photons in the RICH. For measured
track slopes (mx, my) different from their true values :
2 detected photons in the RICH. For measured
track slopes (mx, my) different from their true values :
